Merchandise Inventory: Definition, Importance, Calculation and Examples in 2023
In the United States, only 43% of small businesses track inventory either manually or not at all, which can seriously hinder their capacity to operate profitably in the long run. Operations that don’t manage their inventory are more prone than those that do experience inventory forecasting issues, which may result in higher inventory carrying costs, unanticipated stockouts, or an abundance of unsold inventory. No matter the size or business, inventory is a valuable asset for the firm’s balance sheet.
Merchandise Inventory is a crucial accounting tool that may be used at every level of the manufacturing process to connect production with order processing. This critical source of revenue is essential to a business’s commercial operations and directly impacts how well it performs in terms of fulfillment. Regarding selling the inventory, manufacturers’ inventory differs from merchandise inventory. While merchandise inventory concentrates on purchasing the completed items, manufacturers’ inventory creates the inventory.
Effective inventory management is one of the cornerstones of business success for distributors, wholesalers, and retailers. These businesses frequently have substantial sums of money invested in stocks meant for consumer purchase. But, of course, the most significant asset for many companies is their inventory ready for sale or retail merchandise; car dealers, for instance, may have millions of dollars invested in their vehicle inventory.
- What is Merchandise Inventory?
- Objectives of Merchandise Inventory
- Importance of Merchandise Inventory in Accounting in 2023
- Methods of Valuing Your Inventory for Accounting
- Methods To Measure Merchandise Inventory in 2023
- How is Merchandise Inventory Calculated and Tracked?
- Conclusion: Use InventoryLogIQ to Keep Track of Your Merchandise Inventory in 2023
- Merchandise Inventory: FAQs
What is Merchandise Inventory?
The word “merchandise inventory” refers to the items that wholesalers, retailers, and distributors purchase from suppliers and manufacturers intending to sell. Finished items or raw materials prepared for sale and intended for resale to clients can be included in the merchandise inventory. All items bought but not yet sold are included in the merchandise inventory. This unsold inventory is a current asset on a company’s balance sheet.
Inventory of goods falls within the concept of existing assets since it is typically anticipated that businesses would sell their stock within a year via routine business activities. In addition, the total amount paid to suppliers for the completed items/raw materials, as well as any related expenses, such as insurance, shipping, and storage, are included in the value of the inventory of goods. The profitability, competitiveness, customer happiness, and, ultimately, the existence of a business may all be impacted by how well it manages its merchandise inventory.
Objectives of Merchandise Inventory
An internet business’s most noticeable present asset is its merchandise inventory, which directly affects its performance. Therefore, for correct calculations relating to total costs, assets, and profitability, the company needs to understand the process of merchandising inventory. Additionally, the expertise necessary for accurate computations aids a corporation in comprehending the crucial associated financial factors. Here are the main objectives of merchandise inventory:
Determining Gross Income
The gross profit, the difference between sales and the cost of goods sold, is calculated using inventory. Then, the cost of goods sold is compared to the revenue for the accounting period to estimate the gross profit or trading profit. Opening stock plus purchases less closing stock equals to cost of goods sold. The calculation demonstrates how inventory value influences cost and gross profit. For instance, if the closing stock is overpriced, the gain for the current year will increase while the profit for the years after will decrease.
Analyze The Financial Situation
A current asset is designated as closing stock. The closing stock value determines the company’s financial status on the balance sheet. The working capital situation and the overall financial position might be misrepresented by overvaluation or undervaluation.
Prevention of Insufficient Inventory Stocks
For most firms, running out of inventory may be a fatal mistake. Understocking decreases client loyalty to your brands and directly affects company revenue. Additionally, failing to satisfy clients owing to a lack of inventory puts your company on a fast track to losing its favourable brand reputation. Thus calculating merchandise inventory is beneficial in maintaining inventory levels, which helps the organization in the long run.
Importance of Merchandise Inventory in Accounting in 2023
Since product inventory is typically one of an online brand’s most valuable assets, maintaining precise inventory management and tracking is essential since it directly influences a brand’s financial health. Engaging a CPA when your firm expands is crucial since inventory accounting may be a challenging business procedure to handle.
However, it doesn’t imply there aren’t resources a company can use, such as knowing inventory turnover rate and other crucial inventory reporting indicators, to maintain product inventories better. You may lower your risk of inventory loss, stockouts, and holding too much inventory by prioritizing item inventory control and management. An indication of how liquid your inventory is, for instance, is the turnover of your item inventory. The absence of unnecessary financial ties to dead stock inventory, which also raises carrying costs, is demonstrated by a greater turnover rate.
Once the inventory has been sold, the cost of goods sold (COGS), also known as the logistical cost of procurement, is considered to calculate gross profit. Several alternative inventory valuation techniques (such as FIFO method for inventory valuation) may be used to track inventory and its worth. It depends on your business which option makes sense, given the advantages and downsides of each approach. You must regularly use your chosen technique to ensure accuracy in reporting inventory.
Methods of Valuing Your Inventory for Accounting
First In, First Out (FIFO)
The First-In, First-Out (FIFO) strategy works well to maintain a high level of profitability and a fresh inventory of goods. The company may ensure that the shipments are of the best quality by prioritizing the sale of the first-acquired goods over the purchase of later-acquired goods. When selling seasonal items, FIFO enables a business to value its inventory by calculating the cost of goods sold from the first item it purchased and using that figure to value the remaining stock. This guarantees that profits continue to increase despite changes in the market. As a result, FIFO makes the company more efficient and profitable.
Last In, First Out (LIFO)
The LIFO approach assumes that the most recent additions to the goods inventory will be sold first. Therefore, businesses that specialize in non-perishable goods benefit the most from LIFO. However, the cost disparity between the pricing of the items in the current market and those in the previous one can raise COGS and lower gross profit margins.
Weighted Average Accounting Method
The average cost of things throughout a company’s accounting period is the main foundation of the intermediate cost inventory accounting technique. It is distinct from the previous two methods in that it does not keep track of the cost per inventory unit for every purchase or delivery. Instead, dividing the cost of the goods in the merchandise inventory offered for sale by the total inventory available will get the weighted average.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
In the just-in-time approach, merchandise is only bought as required rather than being held on hand. This can help firms with erratic sales since it keeps them from having too much inventory. In addition, this approach lowers risk, storage overhead costs, and wasteful loss from unsold goods.
Specific Identification Method
Every item in the product inventory is tracked using the specified identifying technique from purchase to sale. The method functions well for inventories of large, readily recognized objects with various attributes and prices. However, the strategy necessitates businesses tracking each item individually using an RFID tag, the particular ID affixed to objects that offers the most precise inventory carrying cost and profit record. The unique identification approach increases the accuracy of the inventory valuation process, but it is mainly limited to valuing expensive and unusual things like real estate, jewellery, and cars.
ABC Analysis
Using the ABC Analysis, a firm may decide which products to sell first based on the cost of goods sold (COGS). The product inventory is divided using this manner into three separate groups:
- A: High-value, low sales: consists of the inventory of goods, which generates a healthy profit but requires considerable upfront expenses. An extended stay with this group may put a burden on finances.
- B: middle-value, average sales: Consists of products with a stable foundation and infrequent sales.
- C: Low-value, high-sale products in the inventory make up category C, which boosts the balance sheet without adding much to profit margins.
Methods To Measure Merchandise Inventory in 2023
After selecting a methodology, you must choose a system that establishes how frequently you will monitor inventory value. An infrequent physical count is a “periodic inventory system” carried out by hand. Real-time inventory management is regarded as a permanent approach, which is more prevalent in inventory accounting since it takes less time and is more precise. This is particularly true if your company has to track every item as it passes through your eCommerce supply chain. Here are the methods to measure your merchandise inventory:
Perpetual Merchandising Inventory
The perpetual merchandising inventory system is the most popular technique businesses use to track all aspects of merchandising inventory in real-time. Companies must constantly update the data on the goods being sold as part of the perpetual inventory method. The firm can examine the inventory activities and transactions during the accounting period thanks to frequent updates on financial reports. The following transactions were made within the time frame:
- Purchases that were recorded as credits to the payable accounts and debits to the inventories
- Purchases that are deducted from the cost of items sold
- Total monies credited to the inventory accounts
- Changes to the quantity debited and recorded in the price of goods sold, as well as credits to the inventory account
- Changes in the placement of inventory
Periodic Inventory System for Merchandising
Companies do not need to maintain an ongoing update of the inventory value and amount when periodically marketing inventory. Instead, a company conducts periodic inventory by taking an inventory report at predetermined intervals to monitor changes to the merchandising inventory. In particular accounting cycles, the procedure involves manually accounting for and comparing the inventory. Organizations that use periodic inventory include:
- Small businesses can manually account for their inventory within the required time frame.
- Businesses have no resources to invest in inventory automation hardware and software.
- Businesses that offer lower-quality goods in large quantities, such as hardware stores that sell nuts, bolts, nails, and screws or candy shops that sell thousands of chocolates. For small enterprises, when the inventory loses some value with consecutive transactions, permanent merchandising inventory management appears to be redundant.
The procedures used for periodic merchandising inventories are frequently incorrect and subject to human error. As a result, this inventory system cannot give the organization any real-time insights into its cost of goods sold, turnover rate, or other inventory indicators.
How is Merchandise Inventory Calculated and Tracked?
The examples below show how a store determines and tracks item inventory to help you understand merchandising better:
Let’s say a business that sells cleaning supplies in bulk is figuring out how much inventory it has. The accountant consults several sections of the balance sheet to determine the current worth of the company’s inventory on hand. The accountant uses the following financial information:
- Beginning Merchandise Inventory
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- Ending Inventory
Beginning Merchandise Inventory Calculation
The value of the inventory at the beginning of the accounting period is referred to as the beginning merchandise inventory or opening merchandise inventory. Before any new inventory is purchased or the current inventory is sold, the opening merchandise inventory value is determined. The ending merchandise inventory value from the prior accounting cycle is included in the beginning Inventory for the current accounting cycle.
Beginning Inventory = (Ending Inventory + COGS) – Purchased Inventory
Calculating The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
The overall cost of producing the finished goods inventory of commodities, including labour, raw materials, etc., is calculated as the cost of goods sold. The primary method of valuation used to estimate how many gross profits were generated by a single or series of sales is COGS.
Cost Of Goods Sold = (Beginning Inventory Cost + Purchases Cost) – Ending inventory
Calculating the Ending Inventory
Since it is the last quantity to be reported on the balance sheet for the designated accounting period, merchandise inventory is referred to as the “closing inventory.” This is because the cost of goods sold is subtracted from the initial inventory, and a new amount is added to determine the merchandise inventory (COGS).
Ending Merchandise Inventory = (Beginning Inventory + New Inventory) – COGS
Example of Calculating Merchandise Inventory
An illustration of how a business determines and records its goods inventory is shown below:
Let’s imagine a business that produces and prints T-shirts. The T-shirts are $20 each. 5,000 T-shirts are sold, 800 fresh products are added to the inventory, with 400 items left in stock.
Ending Inventory – 400 x $20 = $8,000
COGS = 5,000× $20 = $100,000
Inventory purchased – 800 x $20 = $16,000
The formula for calculating the starting inventory is:
Beginning Inventory = (Ending inventory + COGS) – Purchased inventory.
Beginning Inventory = ( $8000 + $100,000 ) – $16000 = $92000
Cost of goods available for sale or initial Inventory = merchandise inventory – COGS
Inventory of goods equals ($92,000) – $16,000 = $76,000
As a result, $76,000 worth of merchandise inventory at the firm during a given accounting period.
Use of Merchandise Inventory Once it is Calculated
According to the given example, $76,000 worth of merchandise inventory during the accounting period. The accountant may use this information to decide how to allocate extra resources, distribute cash for essential supplies, and other uses for the company’s earnings. Therefore, understanding the company’s item inventory is critical to correctly assessing the profitability and financial health of the business.
Furthermore, since that is the amount businesses disclose on the balance sheet, accountants frequently see product inventory as the ending inventory balance. As a result, companies may better define revenue targets and inventory management KPIs by using this figure, which indicates how much of their inventory is available for sale.
Conclusion: Use InventoryLogIQ to Keep Track of Your Merchandise Inventory in 2023
The inventory of commodities that a business purchases for resale to clients is known as merchandise inventory. Typically, firms that use inventories of products are merchants and wholesalers. The financial stability of a corporation depends on effective inventory tracking and management. To save costs, boost performance and profitability, and enhance customer happiness and loyalty, a corporation must comprehend and optimize its goods inventory.
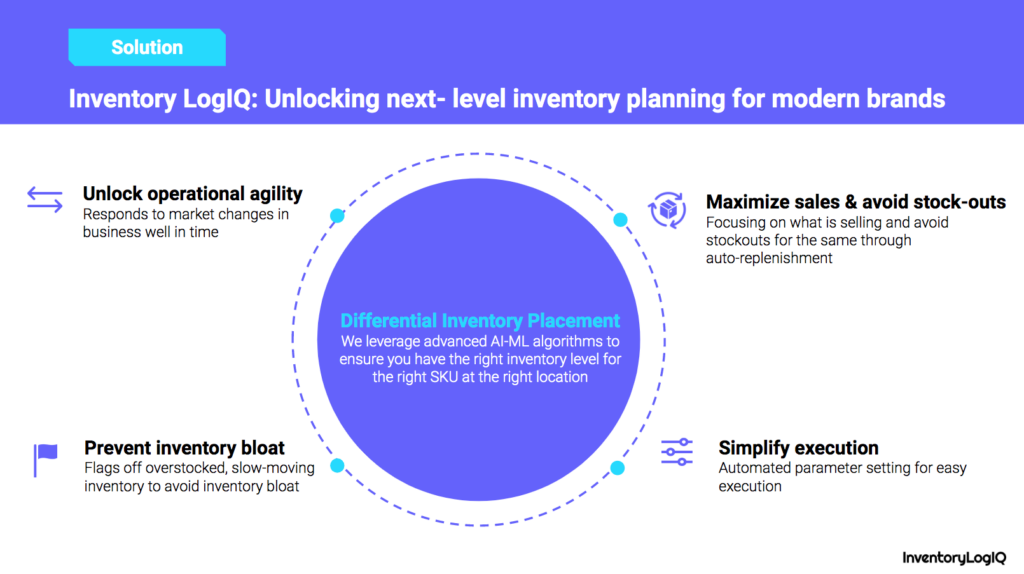
Managing eCommerce logistics operations while your online business grows is challenging since your attention must be directed toward activities generating income. A top-tier inventory management company with a tech-enabled logistics network is InventoryLogIQ. With InventoryLogIQ, you can maintain complete operational visibility and have access to integrated inventory management solutions. Some of the key features we provide a listed below:
Monitoring Stocks In Real-Time
You can quickly track inventory and manage SKUs from the InventoryLogIQ dashboard, giving you total inventory insight in real-time. This will make it easier for you to precisely track inventory flow, storage and inventory warehousing expenses and the typical number of units on hand over time. All of the top eCommerce systems may be connected to InventoryLogIQ within minutes. Once your store is connected and your items are synced, you can:
- View current stock levels by SKU
- Set reorder points for each SKU according to the number you want to receive
- Combine several SKUs for promotions
- Monitor your items across multiple channels
Inventory Optimization
Your order volume will rise as your company expands. However, this may make it more challenging to estimate demand effectively, manage real-time inventory, and optimize inventory storage. With built-in inventory optimization tools, InventoryLogIQ’s inventory management system enables you to estimate demand more accurately, strategically distribute inventory and monitor storage and warehousing costs across fulfillment locations.
Reporting and Analytics
At InventoryLogIQ, we offer an inventory analytics and reporting solution that aids in forecasting future client demand and ideal stock levels. With these insights, you can increase the efficiency of your warehouse and logistics operations, enabling you to exceed client expectations while lowering costs and travel times consistently. Our robust analytics and reporting platform can help you find the answers to queries like:
- What were the historical stock levels for my company at any given period or place?
- How long do I have until an SKU runs out of stock?
- When must I place new orders for each product’s inventory?
- How frequently are certain products sold?
- Which products are not selling and cost a lot to store for eCommerce?








