What is an Inventory Management System? Types, Benefits, and 10 Techniques Used in Inventory Management Systems in 2023
Inventory is constantly changing. Sales, refunds, new receipts, and even damage and theft influence your inventory levels throughout the day. Therefore, the inventory management system is the most crucial part of a successful retail or wholesale organization, notwithstanding their difficulty.
As your business grows and the amount of inventory you handle grows, it becomes challenging to manage inventory effectively. Using technology will make things easier for you and your employees. That is the reason any retail firm needs an inventory control system.
A lot of people associate inventory management with retail applications. However, inventory management systems are used in various industries, including manufacturing, utilities, healthcare, education, government, and more. It simplifies and consolidates the process of regulating inventory movement and maintenance so that the proper inventory quantity is accessible at the right time and in the appropriate condition.
- What is an Inventory Management System (IMS)?
- 8 Benefits Of Inventory Management System
- Types of Inventory Management Systems
- How to Choose an Inventory Management System in 2023?
- 10 Techniques Utilized In Inventory Management Systems
- Partner with InventoryLogIQ for the Best Inventory Management System
- Inventory Management System FAQs
What is an Inventory Management System (IMS)?
An inventory management system or IMS is a system that combines technology, i.e., hardware and software, with processes and procedures to oversee the monitoring and maintenance of stocked products, whether they’re company assets, raw materials and supplies, or finished goods ready to be sent to vendors or end customers. A complete IMS includes the following components:
- A method for identifying each inventory item and its information, such as barcode labels or asset tags. Inventory control system
- Handheld barcode scanners or cell phones with barcode scanning applications are examples of hardware equipment for reading barcode labels.
- Inventory management software includes the capacity to analyze data, produce reports, estimate future demand, and more.
- Labeling, documenting, and reporting procedures and policies. This should incorporate a proven inventory management strategy like Just in Time, ABC Analysis, First-In-First-Out (FIFO), Stock Review, etc.
4 Basic Functions of Inventory Management System
Modern-day IMS aid in the profitability of your company. You might be squandering money on inventory without even realizing it if you don’t have a system. You may be buying too much or not enough. You can be wasting money counting and valuing your goods. You might also be wasting money by not knowing where your inventory is. Primary Functions Of the Inventory Management System include-
Tracking
An inventory management system’s primary function is to keep track of your items and supplies. When you buy inventory, you need to track when you bought it, when you sold it, and how much you have on hand. It also tells you where your inventory is. This is especially critical if your list is used in many departments. A supply of rubber, for example, may move through manufacture, shipment, and storage before ending up in a warehouse in a distant location. You can track how inventory travels through your firm with the help of a sound system.
Avoiding Redundancy
Duplicate orders can quickly lead to an overabundance of inventory. When an item isn’t where it should be on your storage shelf, and you presume you’re out of stock, you make a new order. An inventory management system prevents duplication by alerting you that you already have the item in stock somewhere else.
Inventory Valuation
An inventory control system can inform you how much you pay for inventory at different times of the year. For example, an inventory control system can track those values and calculate your average cost even if you purchased the same item several times at various prices. This might assist you in determining selling prices and profit margins. So, inventory valuation is a big function.
Counting
You won’t have to pay staff to count products if you physically use an inventory control system. Based on the data in your system, you’ll always know how much you have. This can help you save a lot of money on the payroll for inventory workers.
How Do Inventory Management Systems Work?
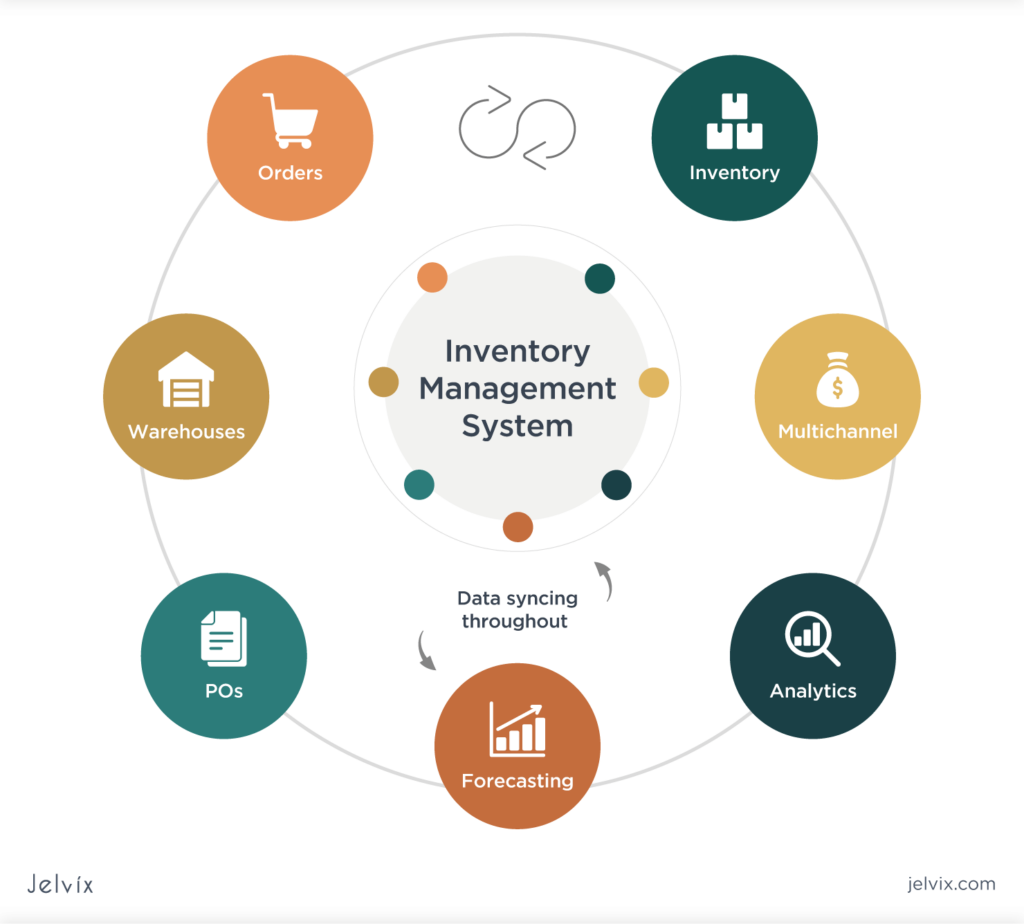
Inventory control systems, such as inventory management applications, include several features that assist businesses in managing various sorts of inventory. For example, inventory management applications are often used with barcode tagging to identify inventory assets, and information about each item is recorded in a central database. Barcode labels act as inventory trackers, allowing users to get information about an item from a computer system, such as the item’s price, the number of units in stock, the position of an object within a warehouse, and so on.
The best inventory control applications are mobile-friendly, with companion apps that let users track and manage inventory while moving about a facility or from one location to another. There are a variety of inventory monitoring apps for smartphones, some of which are only available for mobile devices. In contrast, others feature desktop software that allows users to track inventory from any platform. There are also several inventory management apps created exclusively for warehouse managers. Look for features like trigger warnings when inventory levels hit pre-defined criteria, re-ordering capabilities, and analysis and reporting to support functions like forecasting when looking for inventory management software.
8 Benefits Of Inventory Management System
Any effective business’s inventory management system is what goes on behind the scenes. It’s the art and science of balancing supply and demand in a company – managing the supply chain always to have enough stuff to earn a profit.
For small enterprises or big retail or warehousing operations, using an inventory management system offers several advantages, including:
Automation
Automation is one of its most significant advantages of it. Automation eliminates the possibility of human error, saves countless hours, and assures you that you do not make errors. Once a set of rules has been established, this system can do repetitive tasks with little manual assistance. This gives you real-time access to your inventory levels and instantly changes your stock count when a sale is made. This functionality is essential for accurate inventory forecasting and a positive client experience by preventing overselling. Automated inventory management also provides real-time visibility into where your goods are located, critical to keeping stock in several places, such as a warehouse or multiple retail locations.
Making Informed Decisions
Having enough inventory on hand affects every aspect of a company’s capacity to create profit. Through various built-in reports, the Inventory Management System allows users to make educated decisions based on real-time data from the program. In addition, the Inventory Control System will provide you with the resources to effectively estimate future sales by providing you with a picture of previous sales performance.
Demand Forecasting
Because of precise demand forecasting, when order fulfillment volumes grow significantly due to holidays or events throughout the year, such as a significant marketing push from an influencer, the quantity of inventory you have will stay up with demand. Historical and seasonal data may also determine if any sales patterns necessitate stock level modifications at different periods of the year.
Boost Productivity and Efficiency
By reducing the amount of time spent on routine and complex tasks, the Inventory Management System will help increase efficiency and productivity. Users may easily report, search, and input data and manage inventory using the Inventory Management System’s user-friendly interface.
Boost Sales and Purchase Order Accuracy
Using a sophisticated Order Management System, you can improve the accuracy of sales and buy orders. In addition, users may reserve available goods across various locations with Dynamic Inventory to guarantee that client expectations are satisfied.
Management Inventory of Multiple Locations
When a firm develops into many locations, the owner must be able to keep track of inventory levels at each site. Using Dynamic Inventory’s robust multi-channel sales fulfillment business model, users may monitor inventory levels across various locations.
Attempt to Avoid Running Out of Stock.
Use our Low-Stock Alerts to get alerted when items fall below a certain threshold, ensuring that you don’t run out of stock. In addition, users will now get access to our Low Stock report, which displays all goods that require replenishment, allowing them to prevent running out of stock.
Reduce Risk by Managing Product Recalls Accurately
Users may trace the exact location of items using Lot Numbers, Batch Numbers, and Serial Numbers in the Inventory Management System. This capability comes in handy if you need to enable a product recall for a batch of things.
Types of Inventory Management Systems
Inventory management systems integrate all parts of an organization’s inventory operations, including shipping, purchasing, receiving, warehouse storage, turnover, tracking, and reordering, into a single technological solution. The fact is that an efficient management system takes a holistic approach to inventory and empowers organizations to use lean practices to optimize quality and performance along the supply chain while ensuring the appropriate quantity of stock at suitable locations to deliver the promised services.
The two inventory control systems available and most frequently utilized these days are.
- Perpetual Inventory Management System is one of the most common management systems.
- The second one is called as Periodic Inventory System
Two technological types of inventory management systems utilized to assist the entire inventory management process are-
- Barcode Systems
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Systems.
You must invest in a vertical inventory management system to meet your company’s unique requirements. Finally, we can also divide IMS into industrial sectors. These are further classified into-
- Manufacturing Inventory Management
- Warehouse Inventory Management
- Retail Inventory Management
Organizations must have correct inventory knowledge to be competitive. In addition, making judgments regarding future purchase and distribution duties might be difficult, if not impossible, without knowing what is in storage. Therefore, a comprehensive approach is required to decide how, where, and when to arrange merchandise.
Now that we’ve covered the foundations of inventory control systems and how inventory control systems function in general let’s talk about the types of inventory control systems.
Perpetual Inventory Management System
When inventory goods are acquired, sold from stock, relocated from one location to another, chosen from inventory, and destroyed, a perpetual inventory management system automatically updates inventory records and accounts for additions. Sub certain businesses prefer endless inventory control systems because they provide up-to-date inventory information and manage minimal physical inventory counts. Permanent inventory systems are also favoured for inventory tracking since, when correctly maintained, they provide reliable data regularly. This inventory management system is most effective when combined with a database of inventory amounts and bin locations updated in real-time by warehouse employees using barcode scanners.
Perpetual inventory management systems come with several drawbacks. To begin with, these systems cannot be maintained manually and need specialist equipment and software, resulting in a higher installation cost, particularly for firms with many sites or a variety of warehouses. In addition, maintenance and improvements are required regularly for perpetual inventory management systems, which can be costly. Another disadvantage is that recorded inventory may not represent actual inventory as time passes since frequent physical inventory counts, which are required even when inventory trackers are utilized, are not performed. As a result, mistakes, stolen products, and wrongly scanned things influence inventory records, causing them to differ from absolute inventory counts.
Periodic Inventory System
Periodic inventory systems do not maintain inventory daily; they allow businesses to know the beginning and ending inventory levels over a certain period. Physical inventory counts are used to track inventory in these inventory control systems. When physical inventory is finished, the purchasing amount is transferred to the inventory account, and the cost of the ending stock is modified. Organizations can use LIFO or FIFO inventory accounting methods to calculate the cost of ending inventory or another way; keep in mind that beginning inventory is the previous period’s ending inventory.
The use of a periodic inventory method has a few drawbacks. To begin with, when physical inventory counts are done, routine company operations are almost halted. As a result of the time restrictions, personnel may rush through their physical counts. In addition, because periodic inventory systems do not often employ inventory trackers, mistakes and fraud may be more common due to the lack of continuous inventory control. When adopting a regular inventory management system, it’s also more challenging to pinpoint where inconsistencies in inventory counts arise because so much time passes between counts. Finally, periodic inventory control systems are better suited to smaller enterprises because of the required quantity of labour.
Barcodes Inventory System
In a barcode inventory system, things are given unique barcodes. A barcode is scanned when a product is purchased, and data is sent to a central database.
When choosing a product, the warehouse worker scans the barcode. The scanner then informs the employee if they have chosen the correct item. It also logs the activity in your IMS, allowing you to keep track of stock levels more precisely. Assisting you in keeping real-time inventory track, enhancing picking speed, and also helping in inventory accuracy.
Barcodes may contain much information that your inventory management system can utilize. A barcode, for example, can carry information such as a product’s name, weight, measurements, and warehouse location. However, for efficient choosing, you would often not use a barcode to retain such detailed information but rather a unique string of numbers merely to ensure the correct item is selected.
Barcodes connect the data obtained while picking and packaging to your inventory management system. So, when the barcode is read, it informs the picker that they have selected the correct item and your inventory management system. Then, in your live inventory tracking, reflect the revised value.
On the one hand, it makes life easier for your pickers and reduces mis-picks. But on the other hand, it provides a precise real-time live inventory count.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Inventory Systems
Inventory management systems that employ radio frequency identification (RFID) use active and passive technologies to track inventory movements. Fixed tag readers are used throughout the warehouse using dynamic RFID technology; RFID tags pass through the reader and record the action in the inventory management software. As a result, active solutions are best suited for businesses that require real-time inventory management or where inventory security is a concern. In contrast, passive RFID technology necessitates portable readers to track inventory movement. The inventory management software records the data from a tag when it is read. Passive RFID technology has around 40 feet, while active RFID technology has a reading range of about 300 feet.
RFID-enabled businesses had a 95% inventory accuracy rate.
RFID inventory management solutions come with several drawbacks. For starters, RFID tags are far more expensive than barcode labels. Hence they are often utilized for higher-value items. RFID tags have also been reported to cause interference, mainly when used in many metals or liquids situations. Transitioning to RFID equipment is extremely expensive, and your suppliers, customers, and transportation providers must all have the necessary equipment. Furthermore, RFID tags contain more data than barcode labels, causing your system and servers to become overburdened with data.
Manufacturing Inventory Management System
This is the method you’ll need if your inventory is focused on linking bills of materials and work orders together. To run a manufacturing firm, you’ll need to keep track of your job and the supplies you’ll need to supply or make it, which necessitates a sound inventory management system. These are the characteristics you’ll require:
- Tracking of materials Levels of inventory (parts and finished products)
- ERP/maintenance software connection for automated reordering
Warehouse Inventory Management System
The goal of warehouses is to find out where an item is located. Although maintaining an accurate inventory count of on-hand products is critical, it is also crucial to guarantee that you can find an item quickly in a warehouse scenario. Software-based warehouse inventory management solutions are frequently employed to optimize fulfillment center processes. You’ll require the following features:
- Support in several locations
- System for advanced barcodes (with QR, among other standards)
- Order picking assistance
- Shelf and bin tracking system
Retail Inventory Management System
It’s critical to have adequate stock in a retail firm to keep things running smoothly and financially. Supplies must be reordered before they run out to maximize sales opportunities while avoiding buying too many things that will not be sold. As a result, a sound IMS is necessary to maintain your inventory balanced and in line with your business objectives. These elements are a must-have for ensuring proper inventory levels.
- Order choosing assistance
- Reordering is done automatically.
- Support for barcoding
- Forecasting inventory
How to Choose an Inventory Management System in 2023?
Knowing what you have on hand is the first step in correctly managing your inventory. Depending on the type of your business and the number of things you’re dealing with, you may go as straightforward or as elaborate as you like. A simple logging system may be sufficient for specific firms, while a computerized arrangement is superior for others.
Consumers should consider a few things before deciding on a periodic and perpetual inventory management system technique, as well as a barcode or RFID tagging strategy.
- What is the size of my company?
- I work with what sort of inventory?
- Is there enough money in the budget for a new management system?
- What type of deployment approach should I go with?
After you answer these questions, going further from here will let you dive deeper into concepts to focus on Inventory Management systems.
Manual Inventory Record Keeping
A stock book where you track transactions could suffice if you don’t carry many different things or don’t move many each day. List the types of items in one column, and write down the sales in another. This shows you how many of each item have been sold at a glance. You may accomplish this in a physical notebook or on a computer with a rudimentary spreadsheet. This is the most basic method of inventory management, and it works best when just one or two-person input data and only a few specific things need to be tracked.
There are a few manual logging ways to consider. For example, each sort of merchandise may be tracked using tags, cards, or tickets, which you can record into your log when they sell. You may also determine how much was sold by comparing sales receipts from your cash register with delivery receipts.
Computerized Inventory Management System
It makes sense to bring the speed and usefulness of computers, tablets, and smartphones to inventory management today when most of us are so accustomed to using them. In addition, small business owners will typically profit from a more automated inventory monitoring system. You may spend significantly less time inputting data and obtain far more meaningful information than if you did it manually, with little to no learning curve.
There are several sorts of computerized systems, ranging from tracking inventory through the warehouse and production process to those better suited to retail applications. Some even integrate with your accounting software, automatically updating cash flow figures and income estimates. You can read more in detail about retail warehouses here.
Point of Sales Systems
Your cash register is part of a system that maintains track of your inventory and rings up sales, and calculates the appropriate change using this system. POS systems are particularly useful in controlling inventory and supplies in retail establishments, taverns, and restaurants.
With each sale, you’ll get an updated, real-time picture of where things stand, and you’ll be able to see at a glance which goods are selling and should be reordered and which aren’t and should be lowered to move. In addition, other information, such as consumers’ email addresses or mobile phone numbers, can be entered during a transaction and useful to your marketing efforts.
If you’re thinking about utilizing a POS system, find out what kinds of reports it can generate and how simple it is to use to keep track of your inventory. You want to be able to quickly add new products to your list and create alerts for items that are about to run out.
The software, cash register, receipt printer, bar code scanner, and credit card reader are all included in most POS systems. Start simple and add on as you need it if you can’t afford a full-fledged plan. There are also POS programs for your smartphone that are both free and affordable.
10 Techniques Utilized In Inventory Management Systems
Small businesses frequently have cash flow issues, influencing stock levels, resulting in stock outs and dissatisfied consumers. If too much of this, the company may go out of business. Inventory management system solutions come in handy in this situation.
Business managers may retain ideal inventory counts, eliminate human error, save money for physical inventory stock, and more with the correct inventory control procedures.
Let’s take a look at the most popular inventory methods. These are highly effective methods for improving inventory control in firms.
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
The smallest amount of stock that suppliers are prepared to sell is the minimum order quantity (MOQ). If you can’t meet the minimum order quantity for a product, you won’t be able to buy it from that source.
Suppliers use minimum order numbers to improve earnings while eliminating inventory and “bargain shoppers.”
The minimum order quantity is determined by the entire cost of your inventory and any additional charges you must pay before making a profit. As a result, MOQs help wholesalers stay profitable and maintain steady cash flow.
Economic Order Quantity
The economic order quantity (EOQ) formula helps you balance the expense of keeping goods on hand with a supply chain that satisfies consumer demand. Start with the following information to determine the economic order quantity:
- The pace of demand or the number of goods moved in the previous year (quarter or month, etc.)
- The cost of the things you’ll need to order during the sales period to fulfill demand.
- The expense of storing merchandise at a warehouse (also called the holding cost)
Understanding a product’s EOQ is critical for determining inventory optimization and reorder quantity.
Just In Time Inventory Management
Just-in-time Inventory management comprises producing what’s wanted when required, and in the amounts demanded. Many organizations employ a “just-in-case” inventory management approach, which involves keeping a modest amount of inventory on hand in case of demand increases unexpectedly.
Just-in-time inventory (JIT) management aims to establish a zero-inventory system by manufacturing Goods to Order. It operates on a pull mechanism, which means that when an order is received, it initiates a chain reaction across the supply chain. As a result, employees are notified that inventory must be ordered or that the required items must be manufactured.
A just-in-time inventory management system has several advantages, including:
- Visibility of Inventory that is less old-fashioned, outdated, or spoilt
- Eliminating storage and stacking while optimizing inventory turnover reduces logistics costs and waste production and increases efficiency.
- By lowering your inventory, you may save money on insurance and rent.
- Since manufacturing takes place on a smaller, more concentrated scale, identifying and correcting production problems is faster.
- Keeping a healthy cash flow by only ordering products when it’s essential
FIFO and LIFO
FIFO and LIFO accounting systems are used to value inventories and report profitability.
First in, first out is the acronym for first in, first out. An inventory accounting system states that the first items in your inventory leave instead. Thus it would help if you always got rid of your oldest stock first.
Last in, first out is the acronym ” last in, first out. It is a way of inventory accounting that states that the final goods in your inventory are the first to leave, implying that you get rid of the most recent stock first.
You must always utilize the FIFO rule when running a food business or dealing with perishable goods. You’ll wind up with outmoded inventory, which you’ll have to write off as a loss if you don’t.
When it comes to non-perishable homogenous commodities like brick or stone, LIFO is a fantastic strategy since you won’t have to rearrange your warehouse or rotate batches because they’ll be the first ones out anyhow.
Reorder Point Formula
The reorder point algorithm tells you when it’s time to replenish your inventory. You’ll be notified when you reach the lowest quantity of inventory you can maintain before needing more.
By employing this strategy to order the right amount of stock every month regularly, you may stop becoming a victim of market ups and downs.
ABC Analysis
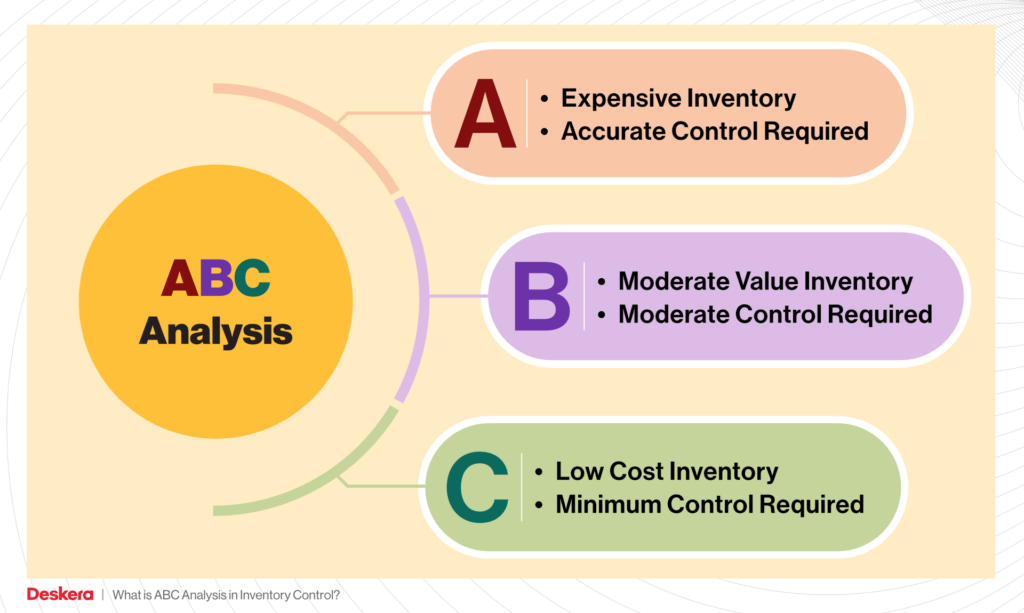
ABC inventory analysis divides your inventory into three groups based on how much it costs to store and how well it sells.
A-Items: The most popular items that don’t take up a lot of room in your warehouse or cost a lot of money.
B-Items: Items in the middle of the price range that sell often but cost more to store than A-Items.
C-Items: The rest of your inventory, which accounts for most of your inventory expenditures, has the smallest impact on your bottom line.
By determining which goods you should refill more regularly and which items you don’t need to keep as frequently, ABC analysis helps you save money on working capital. ABC analysis improves inventory turnover and lowers outdated inventory.
Batch Tracking
Lot tracking is another term for bat tracking. It is a method for effectively tracing items along the distribution chain using batch numbers.
Batch tracking allows you to identify where your items originated from, where they went, how much was sent, and if they have an expiration date, whether they are raw materials or completed things.
This inventory management system has several advantages, including:
- Supplier partnerships have improved.
- Simple and quick recall
- Expiration tracking has been simplified.
- Less accounting mistakes due to manual tracking
Lean Manufacturing System
The lean manufacturing system is also known as lean manufacturing or lean production. This technique is well-known for boosting customer value and eliminating waste without losing efficiency.
It attempts to prevent anything in your production process that generates waste or limits your capacity to make a valuable product, it contributes to inefficient and inconsistent processes.
The following concepts are shared by all lean manufacturing systems:
- The highest valuable product is delivered to the consumer through lean production.
- It outlines the actions and processes necessary to create useful products.
- It goes through a procedure to ensure that all of your value-adding stages run well, with no bottlenecks, delays, or disruptions.
- Products are created on a just-in-time basis, which means that resources are not stored and consumers can get their purchases in weeks rather than months.
- Lean thinking and process improvement are key to the company’s culture.
6 Sigma
Six Sigma practitioners use statistical models to gradually develop and optimize a company’s production process until it reaches the Six Sigma level.
Most commonly, this is accomplished through the use of a five-step method known as DMAIC, which stands for define, measure, analyze, improve, and control.
The DMAIC processes user data and quantifiable objectives to generate a cycle of continuous improvement in manufacturing operations. DMAIC is important for improving existing processes, but Six Sigma also employs DMADV to build new processes, products, or services.
DMADV is an acronym that stands for define, measure, analyze, design, and verify. It serves as data and extensive analysis to assist you in developing efficient procedures or a high-quality product or service.
It uses extensive training and specialized projects, as well as realistic statistical analysis, to help your organization save a lot of money.
Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma combines Six Sigma and lean manufacturing to build a comprehensive system for eliminating waste and reducing process variation to simplify production and improve product output.
Lean Six Sigma largely uses Six Sigma processes as the system’s backbone to generate targeted improvements in production. It also combines several lean tools and approaches to decrease wasted processes and procedures.
Consignment Inventory
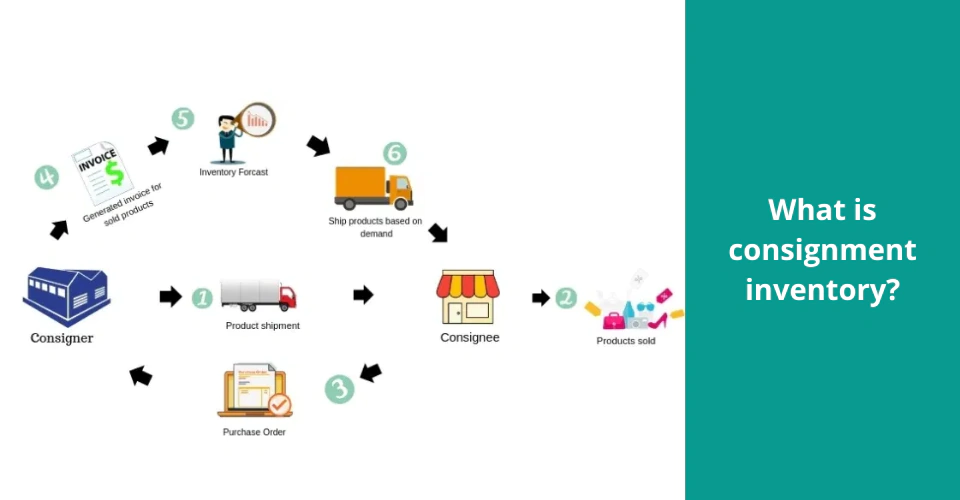
Consignment inventory is a commercial arrangement in which a seller or wholesaler known as a consigner agrees to provide their products to a consignee, most commonly a retailer, without the retailer paying for the items in advance. The co-signer retains ownership of the products and pays for them only when they are sold.
As long as suppliers and retailers are ready to share the risks and profits, this is a win-win situation.
Low inventory carrying costs, direct-to-retailer delivery, and access to new markets benefit vendors. Retailers benefit from reduced risk, greater cash flow, and a cheaper total cost of ownership.
Partner with InventoryLogIQ for the Best Inventory Management System
You can plan your stock levels and know when to place a purchase order for extra products using a proactive inventory management system. You may better manage your cash flow by projecting your inventory demands into the future. Prevent sales from being lost due to stockouts and backorders.
eCommerce fulfillment businesses have never needed to plan more. Inventory management and forecasting aid in developing a robust supply chain that can withstand interruptions.
You don’t have to deal with the difficulties of inventory management systems across numerous sales channels. Request assistance from your third-party logistics provider or seek an inventory optimisation software like Inventory LogIQ.
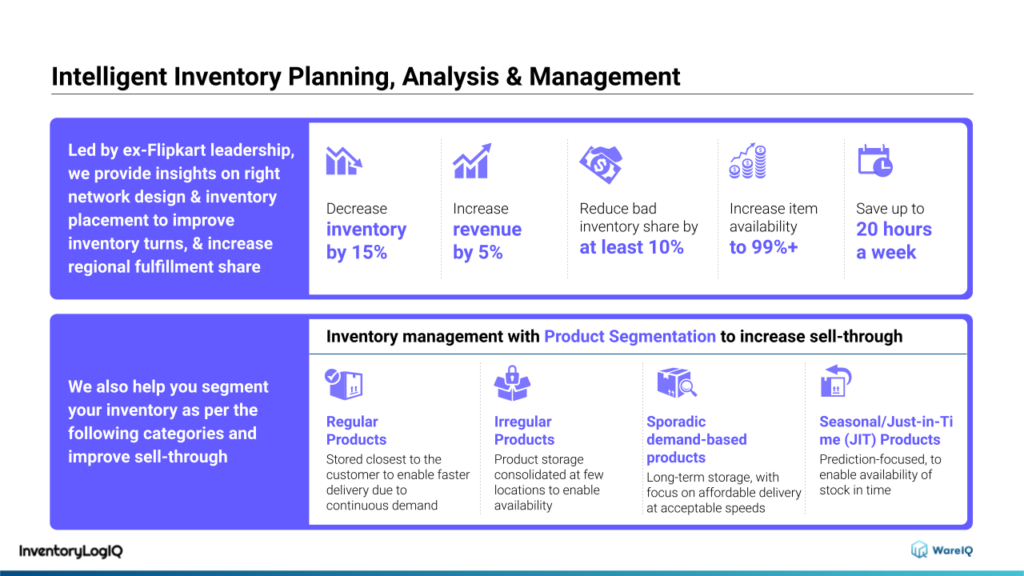
Inventory LogIQ optimizes the distribution of inventory across fulfillment network, that can help in maximizing sales, reducing holding costs and improving regional share of demand fulfillment. These solutions are implemented quickly and operate cost-effectively, saving organizations time, money, and effort. InventoryLogIQ’s extensive knowledge and capabilities in inventory forecasting, product segmentation, and easy plug & play integration offerings enable us to solve all of our clients’ inventory control and management problems.





